Have you ever wondered about the latest advancements in the production of hemp textiles? Well, look no further! In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of technological innovations that are revolutionizing the hemp textile industry. From cutting-edge machinery to sustainable practices, these advancements promise to enhance the quality, efficiency, and environmental impact of hemp textile production. So, get ready to uncover the exciting developments that are shaping the future of this versatile and eco-friendly industry.
The Rising Technological Innovations in Hemp Textile Production
As the demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly textiles continues to grow, the production of hemp textiles is experiencing a significant surge in popularity. Hemp, a strong and versatile natural fiber, offers numerous benefits, including durability, breathability, and hypoallergenic properties. To meet the increasing demand, various technological innovations have emerged in the production of hemp textiles. From advanced fibre processing technologies to sustainable harvesting techniques, this article explores the key advancements shaping the future of hemp textile production.
1. Advanced Fibre Processing Technologies
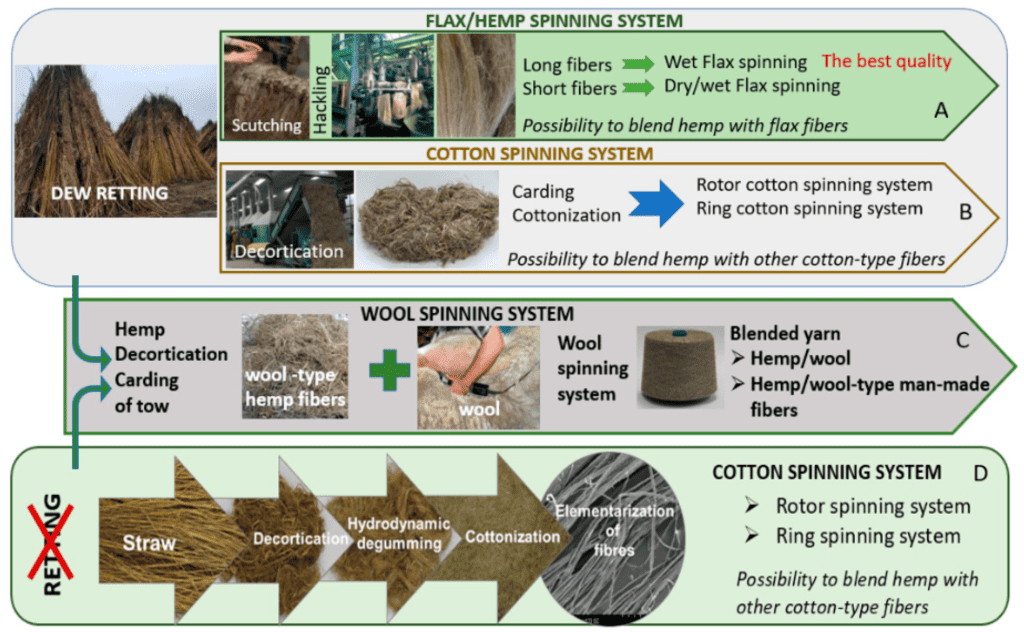
1.1 Decortication
Decortication, the process of separating the outer bast fibers from the inner woody core of the hemp plant, plays a crucial role in the production of high-quality hemp textiles. Advanced decortication machines utilize mechanical or chemical methods to efficiently extract the long and strong fibers, while minimizing damage. These technologies not only enhance the productivity and efficiency of the decortication process but also ensure the preservation of the fiber’s integrity.
1.2 Enzyme Treatment
Enzyme treatment is increasingly embraced as a method to improve the fiber quality and dye uptake of hemp textiles. Enzymes are used to break down the pectin and lignin present in hemp fibers, resulting in improved softness, flexibility, and dye absorption. This process not only enhances the overall quality of the hemp textiles but also reduces the environmental impact by minimizing the use of chemicals.
1.3 Mechanical Processing
Mechanical processing techniques, such as combing and carding, are employed to align and separate the individual hemp fibers, ensuring uniformity and strength in the final textile product. Innovations in mechanical processing have led to the development of advanced machines that are capable of handling the tough and long fibers of hemp more effectively, resulting in increased yarn quality and production efficiency.
1.4 Biochemical Processing
Biochemical processing methods, including microbial retting and bacterial degumming, are gaining traction in hemp textile production. These processes utilize natural organisms to break down the pectin and other impurities in the hemp fibers, resulting in increased softness and improved coloration. Biochemical processing offers a more sustainable alternative to conventional chemical-based methods, reducing the environmental impact of textile production.
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
2. Improved Hemp Strains
2.1 Genetic Modification
Genetic modification techniques are being employed to develop improved hemp strains with enhanced fiber quality, growth rates, and resistance to pests and diseases. By manipulating the plant’s DNA, scientists can introduce desirable traits into the hemp plant, ensuring greater productivity and sustainability in hemp textile production. However, it is important to carefully consider the environmental and ethical implications associated with genetic modification.
2.2 Hybridization
Hybridization, the crossbreeding of different hemp varieties, is another method used to improve hemp strains for textile production. By selectively combining the traits of different hemp plants, breeders can develop hybrids that exhibit superior fiber quality, yield, and adaptability to different climatic conditions. Hybridization allows for the creation of hemp strains that are tailor-made for specific textile production requirements.
2.3 Phenotypic Selection
Phenotypic selection involves the careful observation and selection of hemp plants based on their physical characteristics, such as fiber strength, color, and length. By focusing on the traits exhibited by individual plants, breeders can identify and propagate superior hemp varieties that are better suited for textile production. Phenotypic selection offers a more natural and environmentally friendly approach to improving hemp strains without resorting to genetic modification.
3. Sustainable Harvesting Techniques
3.1 Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture techniques, such as satellite-guided seeding and automated irrigation systems, are being employed to optimize hemp cultivation and harvesting. These technologies enable farmers to accurately control the amount of water, nutrients, and pesticides used, minimizing waste and environmental impact. Precision agriculture ensures optimal crop yield while reducing the reliance on harmful chemicals and preserving soil health.
3.2 Drone Technology
Drones equipped with specialized cameras and sensors are revolutionizing hemp cultivation and harvesting. These airborne devices provide farmers with valuable insights into crop health, growth patterns, and pest infestations. By gathering precise data, drones enable farmers to make informed decisions regarding crop management, resulting in increased productivity and sustainable hemp cultivation practices.
3.3 Satellite Imaging
Satellite imaging technologies are used to monitor hemp fields on a large scale, providing valuable data on crop health, growth, and overall conditions. By analyzing satellite images, farmers and researchers can identify areas of concern and implement targeted interventions to optimize crop yield and minimize environmental impact. Satellite imaging enables more efficient and sustainable hemp cultivation practices on a global scale.
This image is property of mariposatechnology.com.
4. Smart Fabric Manufacturing
4.1 Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is being leveraged to develop innovative textiles with enhanced properties. By manipulating materials at the nanoscale, researchers can enhance the strength, durability, and functionality of hemp fibers. Nanotechnology enables the production of fabrics with self-cleaning, antimicrobial, and UV-resistant properties, expanding the range of applications for hemp textiles and driving the development of sustainable and high-performance textile products.
4.2 3D Printing
3D printing technology is revolutionizing the manufacturing process of textiles, including hemp textiles. By layering and bonding individual fibers or filaments, 3D printers can create complex and customizable textile structures with precise control over the fabric’s properties. This additive manufacturing approach not only reduces waste and energy consumption but also allows for the creation of intricate designs and patterns, opening up new possibilities for hemp textile production.
4.3 Smart Sensors
Smart sensors embedded within textiles are enabling the development of intelligent and interactive hemp fabrics. These sensors can monitor various parameters, such as temperature, moisture, and movement, providing valuable data for applications in sports, healthcare, and smart clothing. By integrating smart sensors into hemp textiles, manufacturers can enhance comfort, performance, and functionality while promoting sustainable and eco-friendly textile production.
4.4 Conductive Fibers
Conductive fibers, made possible through advancements in materials science and engineering, allow for the integration of electronics and smart technology into hemp textiles. These fibers enable the creation of wearable technology, such as smart garments and accessories, that can monitor biometric data, provide haptic feedback, and even charge electronic devices. The incorporation of conductive fibers in hemp textiles represents a significant advancement in the development of sustainable and high-tech fabrics.
5. Waterless Textile Dyeing
5.1 Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Dyeing
Supercritical carbon dioxide dyeing is an innovative and sustainable alternative to traditional water-based dyeing methods. By utilizing carbon dioxide in its supercritical state, dye molecules can be efficiently dispersed and absorbed by the textile fibers, eliminating the need for water and reducing the environmental impact of dyeing processes. This waterless dyeing technique offers significant energy and water savings, making it an attractive option for sustainable hemp textile production.
5.2 Cold Pad Batch Dyeing
Cold pad batch dyeing is another water-saving dyeing method that is gaining popularity in hemp textile production. This technique involves the application of reactive dyes onto the fabric using a cold pad, followed by a curing process. Cold pad batch dyeing eliminates the need for high temperatures and large volumes of water, resulting in reduced energy consumption, increased dye fixation, and improved color fastness.
5.3 Plasma Dyeing
Plasma dyeing is a sustainable dyeing technique that utilizes plasma technology to transfer color onto textile fibers without the need for water or chemicals. By creating a plasma discharge, the dye molecules are activated and permanently bonded to the fabric’s surface, providing vibrant and long-lasting colors. Plasma dyeing offers numerous environmental benefits, including water and energy savings, minimized chemical usage, and reduced wastewater pollution.

This image is property of assets.website-files.com.
6. Blockchain Tracking and Traceability
6.1 Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology is being utilized to enhance supply chain transparency in the hemp textile industry. By recording and securely storing information at every stage of the production and distribution process, blockchain enables stakeholders to verify the authenticity, quality, and sustainability of hemp textiles. This transparency fosters trust and confidence among consumers and facilitates the implementation of ethical and sustainable practices within the industry.
6.2 Product Authentication
Blockchain technology can also be employed for product authentication, protecting hemp textiles from counterfeiting and ensuring the integrity of the supply chain. Each hemp textile product can be assigned a unique digital identifier that is linked to a blockchain record, containing information about its origin, production methods, and certifications. This authentication system not only safeguards consumer interests but also encourages responsible and sustainable production practices.
6.3 Quality Control
Blockchain technology offers a robust solution for enhancing quality control procedures in hemp textile production. By integrating real-time data from various stakeholders, such as fiber suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, blockchain systems enable traceability and accountability throughout the production process. This ensures adherence to quality standards, reduces the risk of defects or inconsistencies, and ultimately improves the overall quality of hemp textiles.
7. Intelligent Quality Control Systems
7.1 Computer Vision Technology
Computer vision technology is revolutionizing quality control processes in hemp textile production. By utilizing advanced cameras and image analysis algorithms, manufacturers can automate the inspection of fibers, yarns, and fabrics, detecting defects or inconsistencies with high accuracy and speed. Computer vision systems greatly enhance production efficiency, reduce waste, and ensure the delivery of high-quality hemp textile products to consumers.
7.2 Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms enable intelligent and adaptive quality control systems in hemp textile manufacturing. These algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data collected during the production process, identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies that may indicate quality issues or inefficiencies. By continuously learning and adapting, machine learning algorithms facilitate real-time decision-making, leading to improved product quality, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction.
7.3 Automated Inspection
Automated inspection systems, equipped with robotics and sensors, are replacing manual inspection methods in hemp textile production. These systems can monitor various parameters, such as color, thickness, and defects, ensuring that the final products meet the desired specifications. Automated inspection reduces human error, increases productivity, and improves consistency in quality control, contributing to the overall efficiency and sustainability of hemp textile manufacturing.

This image is property of wordpress.textileworld.com.
8. Energy-Efficient Hemp Textile Production
8.1 Solar-Powered Machinery
Solar-powered machinery is being increasingly adopted in hemp textile production to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and minimize carbon emissions. By harnessing solar energy, machines used in decortication, spinning, weaving, and other production processes can operate without contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Solar-powered machinery contributes to the development of a more sustainable and environmentally friendly hemp textile industry.
8.2 Energy Recovery Systems
Energy recovery systems, such as heat exchangers and waste heat recovery units, are essential in optimizing energy usage in hemp textile production. These systems capture and reuse the heat generated during various manufacturing processes, reducing the overall energy consumption and improving the energy efficiency of production facilities. Energy recovery systems contribute to cost savings and promote sustainable energy practices within the industry.
8.3 Optimization of Production Processes
The optimization of production processes is a key area of focus for energy-efficient hemp textile production. By analyzing and re-engineering manufacturing processes, manufacturers can identify energy-intensive stages and implement energy-saving measures, such as process automation, equipment upgrades, and improved insulation. Optimization efforts lead to significant energy savings, reduced environmental impact, and increased overall sustainability in hemp textile production.
9. Sustainable Finishing Technologies
9.1 Enzymatic Finishing
Enzymatic finishing techniques are gaining traction as a more sustainable alternative to conventional chemical-based finishing processes. Enzymes are used to modify the surface properties of hemp textiles, enhancing attributes such as softness, water repellency, and color fastness. Enzymatic finishing not only reduces the use of toxic chemicals but also offers greater control, efficiency, and sustainability in the production of high-quality and eco-friendly hemp textiles.
9.2 Biodegradable Coatings
Biodegradable coatings are increasingly utilized in hemp textile finishing applications to improve fabric properties and impart specific functionalities. These coatings are derived from natural and renewable sources, such as plant-based materials or biopolymers, and are designed to degrade and break down harmlessly in the environment. Biodegradable coatings provide an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional chemical coatings, minimizing the ecological footprint of hemp textile production.
9.3 Low-Impact Printing Techniques
Low-impact printing techniques, such as digital printing and water-based inks, are becoming more prevalent in hemp textile production. These techniques minimize the use of water, energy, and chemicals traditionally associated with textile printing processes. Digital printing allows for precise color application without the need for screens or plates, reducing waste and enabling customization. By adopting low-impact printing techniques, manufacturers can enhance their sustainability practices and offer eco-friendly hemp textile products.

This image is property of www.startus-insights.com.
10. Robotic Automation in Manufacturing
10.1 Robotic Sewing
Robotic sewing systems are transforming the manufacturing process of hemp textiles with increased speed, accuracy, and efficiency. These automated systems are capable of performing complex sewing tasks, such as stitching intricate patterns or attaching fasteners, with precision and consistency. Robotic sewing not only reduces labor costs and production time but also improves the overall quality and sustainability of hemp textile manufacturing.
10.2 Automated Material Handling
Automated material handling systems streamline the movement of materials and products within hemp textile manufacturing facilities. These systems utilize robotics and conveyance technologies to transport, sort, and store raw materials, components, and finished products. By automating material handling processes, manufacturers can enhance efficiency, reduce labor requirements, and minimize the risk of damage or waste, contributing to sustainable and cost-effective hemp textile production.
10.3 Collaborative Robots
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are revolutionizing the manufacturing industry, including hemp textile production. These robots are designed to work alongside human operators, assisting in various tasks such as material handling, quality control, and assembly. Cobots offer the benefits of increased productivity, improved ergonomics, and reduced safety risks. The integration of collaborative robots in hemp textile manufacturing promotes sustainable and efficient production practices while ensuring a safe and productive working environment.
In conclusion, the rising technological innovations in hemp textile production are transforming the industry by enhancing the efficiency, sustainability, and quality of hemp textiles. From advanced fibre processing technologies to sustainable harvesting techniques, smart fabric manufacturing, waterless textile dyeing, and robotic automation, these advancements are driving the development of a more eco-friendly and socially responsible textile industry. As the demand for sustainable textiles continues to grow, the integration of these innovative technologies into hemp textile production will play a vital role in shaping the future of the industry.
Recent Posts
Discover how bubble hash is rated on a 1 to 6 scale. From texture and color to aroma and potency, learn the key factors that determine the quality of bubble hash. Whether you're a seasoned cannabis...
Looking to learn about the most popular style of hash? This article explores the different types, from traditional to bubble hash, and reveals the people's favorite. Join us on a journey through the...

